Lexicography
Lexicological research and producing Dictionaries
Felix Rau University of Cologne
- Purpose of dictionaries
- Types of dictionaries
- Collecting data for dictionaries
- Structure of dictionaries
- Tools for producing dictionaries
Day 1
Why do you want to make a dictionary?
- for myself in the field
- for the (whole) community
- for semi-speakers
- for learners
- for the general public
- for linguists
- for other scientists
Types of dictionaries
- Audience: speakers vs. scientific audience
- Type: monolingual vs. bilingual (vs. trilingual)
- Form: wordlists vs. dictionaries
- Scope: general vs. thematic
- Perspective: synchronic vs. diachronic
- Medium: print vs. digital
monolingual vs. bilingual
monolingual

bilingual

trilingual
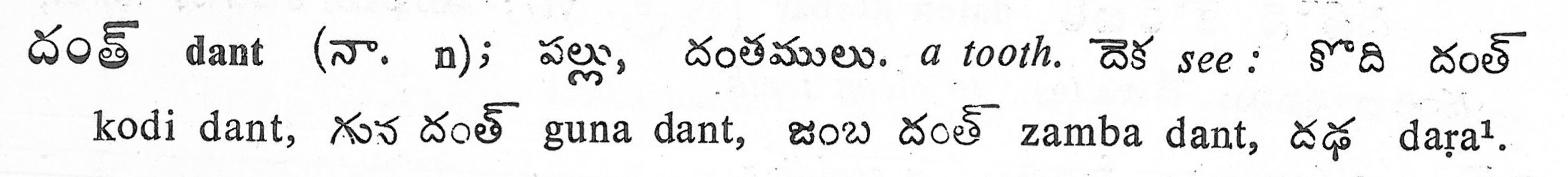
wordlists vs. dictionaries
Wordlist (trilingual)

Dictionary (trilingual)
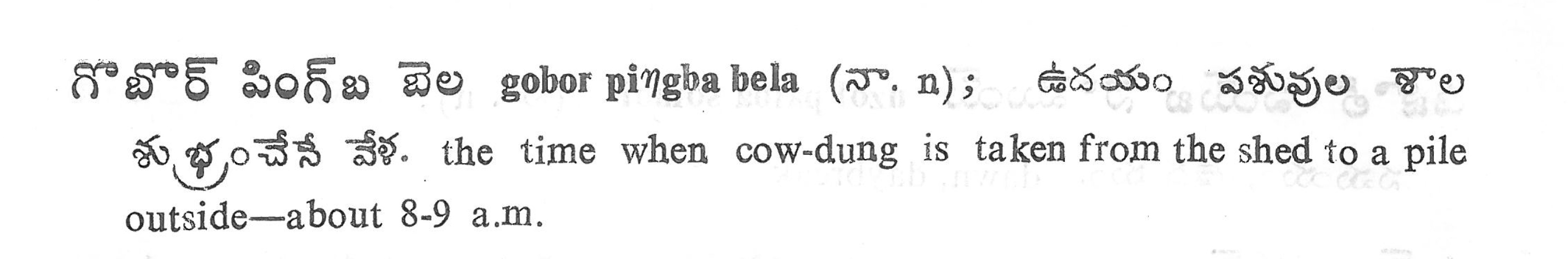
Other types of dictionaries
- encyclopaedic dictionary
- thematic dictionary
- picture dictionary
- etymological dictionary
general vs. thematic
Encyclopaedic dictionaries

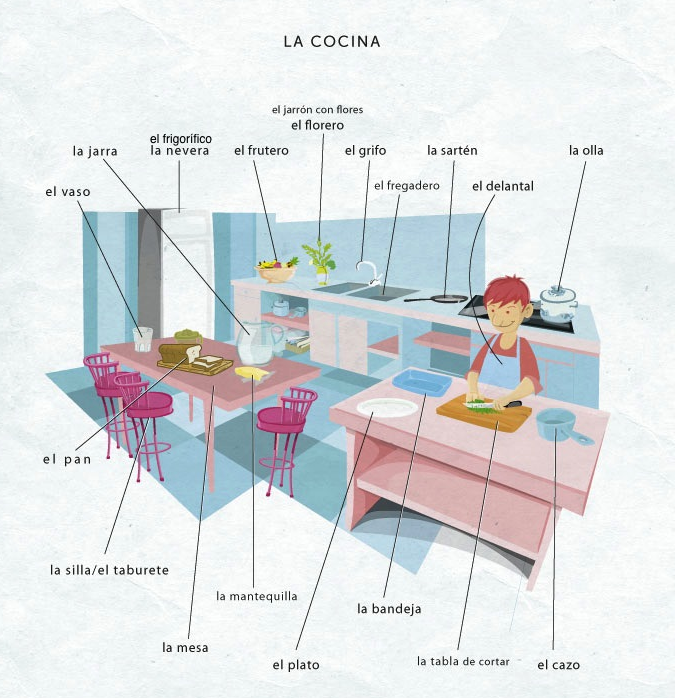
Picture dictionaries
synchronic vs. diachronic
etymological dictionaries

(Burrow, T. and M. B. Emeneau. A Dravidian etymological dictionary. 2nd ed. Oxford: Clarendon Press, 1984.)
cf. A Preliminary Mayan Etymological Dictionary (Kaufman and Justeson 2003)
print vs. digital
non-digital print

Print (self-printed)

Digital (desktop)
Digital (mobile)
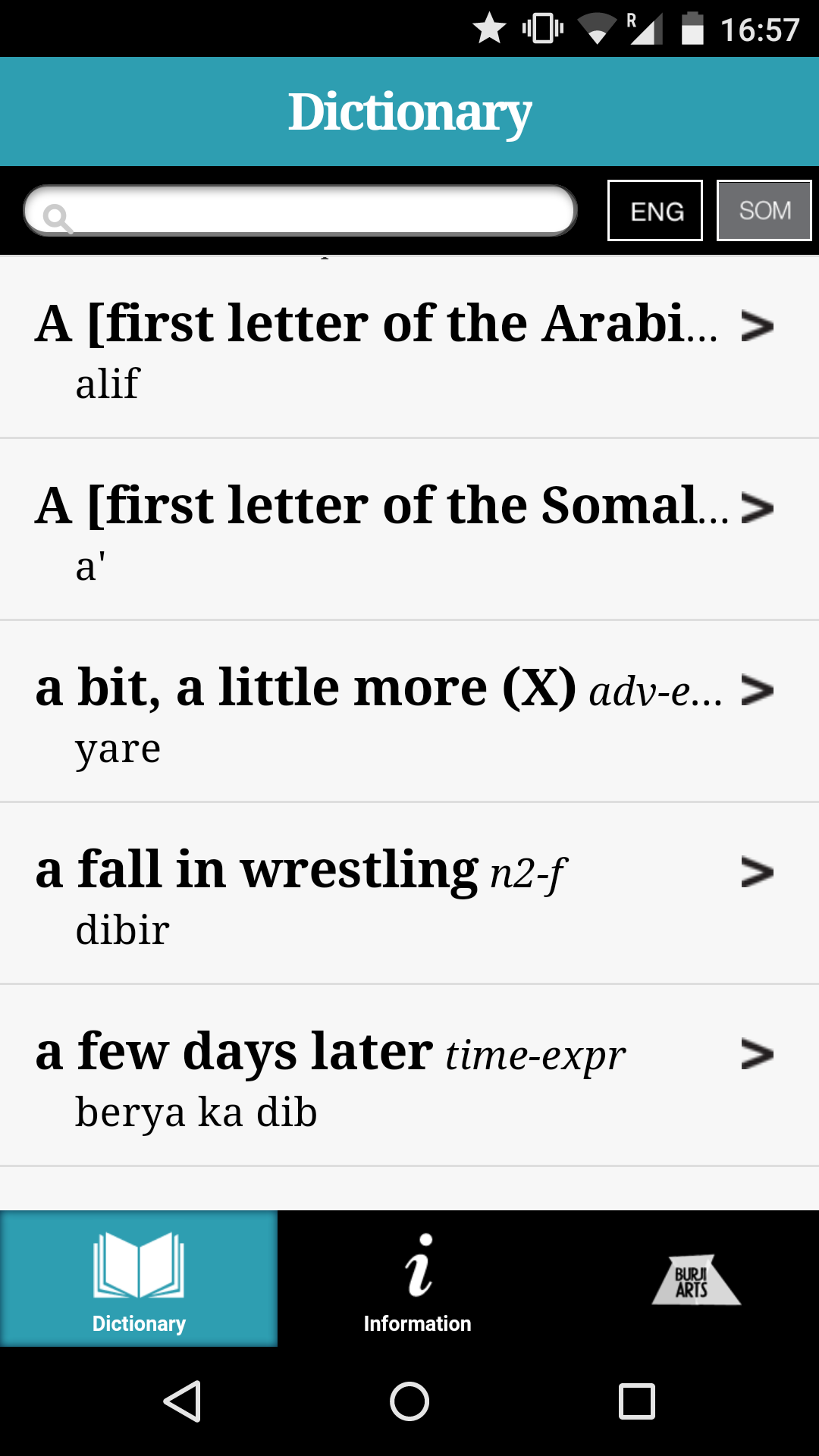
speakers vs. scientific
speakers/learners/community

scientific


Discussion
- What material do you have for your language?
- What do you think is needed most for your language?
- What resources do you have to make a dictionary?